Dunes
Dunes
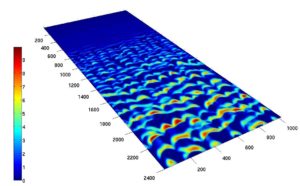
Dunes are ubiquitous on deserts and coastal areas of our planet, as well as on Mars, Venus, Titan and even on the sea bottom. The quantitative understanding of dune morphology and dynamics can help us to develop efficient measures for preventing desertification and to improve our knowledge of sediment transport and wind regimes on planetary surfaces. Using a morphodynamic (continuum) model for sediment transport and dune formation, we investigate the genesis and dynamics of different types of dunes occurring in Nature. Our simulations account for varying flow directions, vegetation growth, groundwater level and topography. Moreover, Computational Fluid Dynamics simulations are used in order to investigate the characteristics of the turbulent fluid flow over the dune profile.
Publications
| Britt Michelsen, Severin Strobl, Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Thorsten Pöschel Two-dimensional airflow modeling underpredicts the wind velocity over dunes Scientific Reports 5, 16572(2015) |
| Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli Rectilinear Dune Encyclopedia of Planetary Landforms. Springer. New York, NY.(2014) |
| Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli Drop Dune Encyclopedia of Planetary Landforms. Springer. New York, NY.(2014) |
| Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli Dome Dune Encyclopedia of Planetary Landforms. Springer. New York, NY.(2014) |
| Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Orencio Durán, Mary C. Bourke, Haim Tsoar, Thorsten Pöschel, Hans J. Herrmann Origins of barchan dune asymmetry: insights from numerical simulations Aeolian Research 12, 121-133(2014) |
| Thomas Päthz, Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Jasper F. Kok, Hans J. Herrmann Analytical model for flux saturation in sediment transport Physical Review E 89, 052213(2014) |
| Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Klaus Kroy, Haim Tsoar, José S. Andrade Jr., Thorsten Pöschel Morphodynamic modeling of aeolian dunes: Review and future plans EPJ Special Topics 223, 2269-2283(2014) |
| Ascânio D. Araújo, Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Thorsten Pöschel, José S. Andrade Jr., Hans J. Herrmann Numerical modeling of the wind flow over a transverse dune Scientific Reports 3, 2858(2013) |
| Thomas Pähtz, Jasper F. Kok, Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Hans J. Herrmann Flux saturation length of sediment transport Physical Review Letters 111, 218002(2013) |
| Mary C. Bourke, Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Shane Byrne, Daniel C. Berman Dune migration in the north polar region of Mars Third International Planetary Dunes Workshop, 7007(2012) |
| Jasper F. Kok, Eric Josef Ribeiro Parteli, Timothy I. Michaels, Diana B. Karam The physics of wind-blown sand and dust Reports on Progress in Physics 75, 106901(2012) |
Posters
 |
Modeling the turbulent wind flow over transverse dunes Ascâno D. Araújo, Thorsten Pöschel, Eric Parteli, José S. Andrade Jr., Hans J. Herrmann |